Trusted for 25+ Years
Labiaplasty

Dr. Lisa Lawless, CEO of Holistic Wisdom
Clinical Psychotherapist: Relationship & Sexual Health Expert

Labia Surgery
Many women opt for plastic surgery on their labia (labiaplasty, vaginal rejuvenation), citing discomfort during sports, embarrassment, and aesthetic reasons as prime motivating factors. Despite the lack of statistics, gynecologists and cosmetic surgeons claim that plastic surgery on labia and vaginas has become a popular trend. Most of these operations are designed to reduce the size (length) of a woman’s inner labia (labia minora) when it is larger or longer than the outer labia (labia majora).
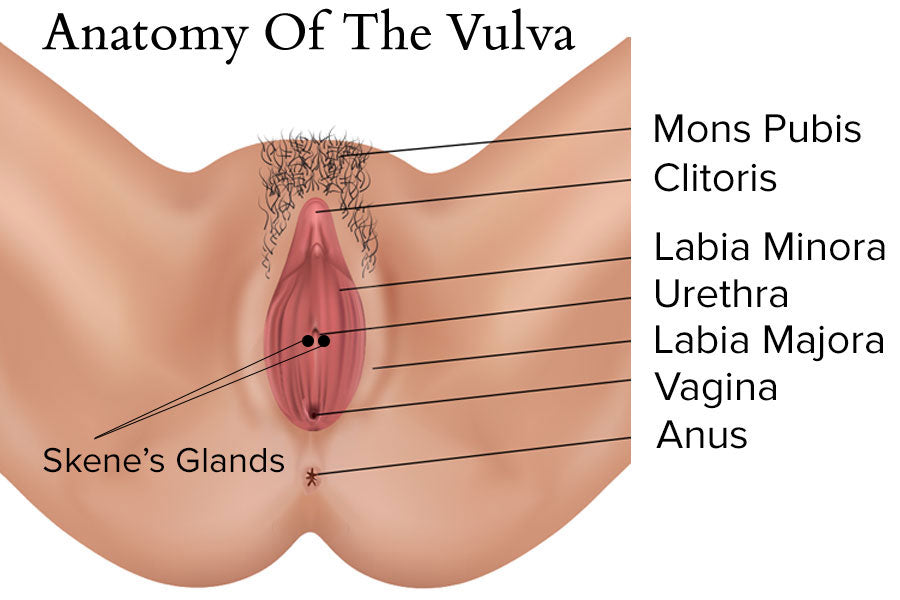
There is a medical term for a large or long labia: labial hypertrophy. It is diagnosed when the labia are much longer than the labia majora. It can be caused by childbirth, accidents, aging, genital piercing, urinary incontinence, lymphatic congestion, chronic dermatitis, myelodysplastic disease, granulomatous disease, use hormones, and genetic predisposition.
Some women that get the surgery have very long labia, while others are asymmetrical (one side is longer than the other). This can cause psychological insecurities about the attractiveness of the labia and health concerns.
Reasons why women opt to get this type of surgery:
- The accidental catching it with a zipper
- Difficulty with hygiene
- Discomfort when wearing tight clothing
- Pain during sports like bicycling and even running
- Difficulty with controlling urinary stream
- Painful sex
Women that have the surgery are just as likely to have it for cosmetic reasons as for health issues, with a 93% rate of patient satisfaction with the outcome. There can be medical complications with labiaplasty, but they are uncommon. The most common complications are infections, excessive bleeding, difficulty with healing, asymmetry, and under and overcorrections. It typically takes 3-7 days for a patient to rest and recover.
Can It Be Medically Necessary?
When the labia is pulled into the vagina during sex, it can result in painful tearing to the vulva tissue making sex challenging. This would be considered medically necessary, as would pain when sitting, walking, running, biking, etc.
How Common Is It?
According to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS), outpatient labiaplasty procedures are done around 10,000 each year.
Risks
- Bleeding, hematoma, and infection
- Decreased vulvar sensitivity
- Chronic dryness
- Numbness
- Scarring
Labia Minora Procedures
- Edge resection is when the labia is shortened by trimming the protruding edges.
- Wedge resection removes wedge-shaped cuts out of the center of the labia minora and suturing the remaining skin together with dissolvable stitches.
Labia Majora Procedures
- Cut tissue or use liposuction to remove excess fat around the labia majora that are longer or fuller than desired.
- Inject fat or fillers to plump up the labia majora that aren’t as full as desired.
In Closing
If you feel that it is medically necessary or that it would improve the quality of your life, you may want to talk with a plastic surgeon to see if you are a good candidate for a labiaplasty. See our helpful guide on How To Talk To Your Doctor About Sex.


